
Before I joined my design school, I felt overwhelmed by the world of art and design jargon.
Did you feel the same way when you started?
If you’re an art and design enthusiast, don’t worry, it’s a common experience.
To help you out, I’ve compiled a list of the 101 most common words designers use in this “Art Vocabulary List”.
I’m here to help you discover the creative terminology word by word so that you can engage in professional conversations with designers and better express your ideas for your projects!
101 Art Vocabulary List | Speak Like a Designer
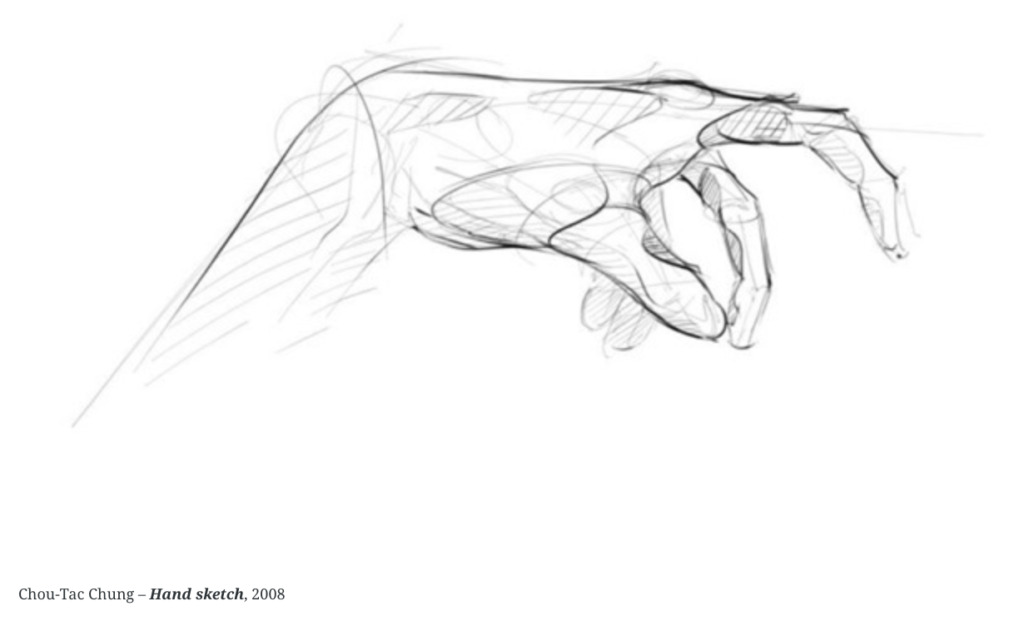
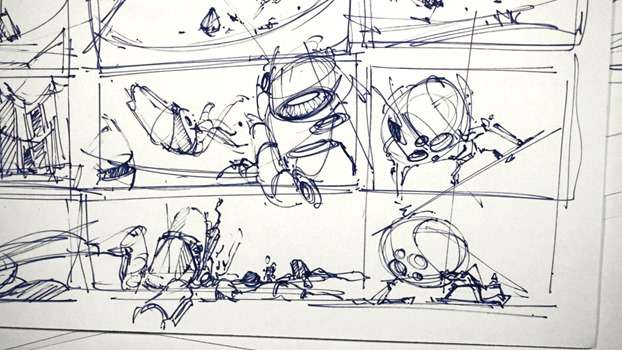
1. What is a Sketch?
- A quick, rough drawing is used to explore and develop ideas.
2. What is Perspective?
- A technique used in sketching to create the illusion of depth and distance in a two-dimensional drawing.
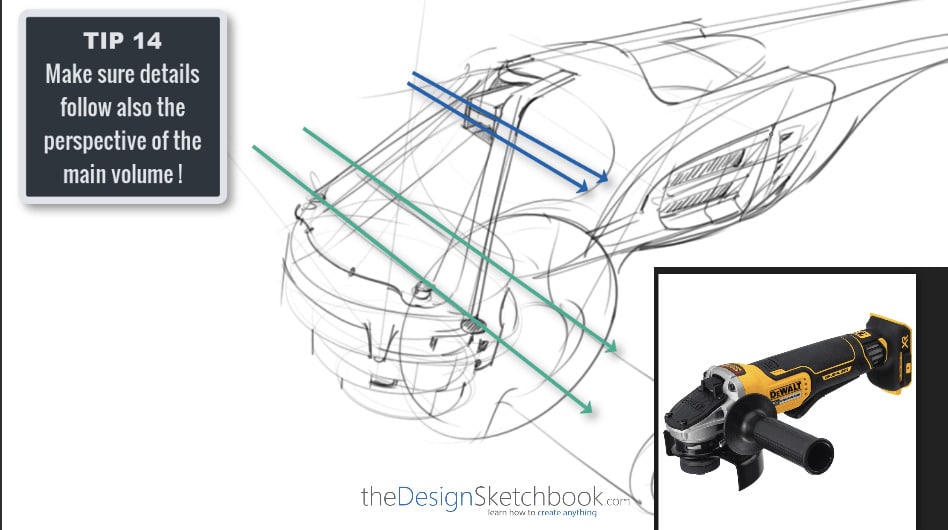
3. What is an Orthographic projection?
- A method of drawing objects in which all the surfaces of an object are projected onto a plane.
4. What is a Thumbnail sketch?
- A small, quick sketch used to explore and develop ideas before creating a more detailed drawing.
5. What is drawing with Line weight?
- The thickness or thinness of a line in a drawing, used to create depth and emphasis.
Whether you’re a beginner artist or an art enthusiast, this vocabulary list helps you speak like a Designer!
6. What is Shading?
- The use of light and dark values to create the illusion of form and depth in a drawing.
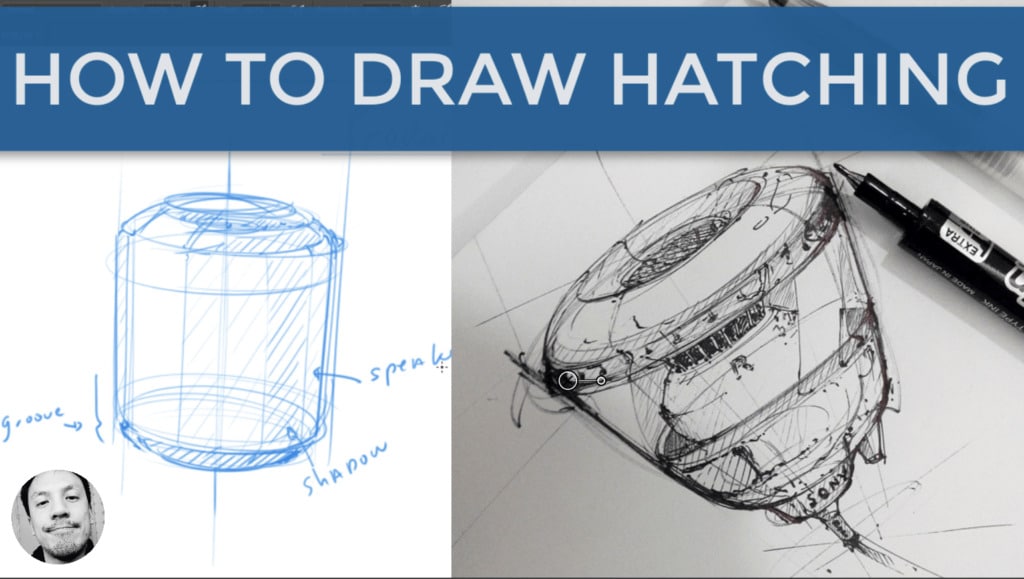
7. What is Hatching?
- A shading technique using closely spaced parallel lines.
8. Cross-hatching
– a shading technique using intersecting sets of parallel lines.
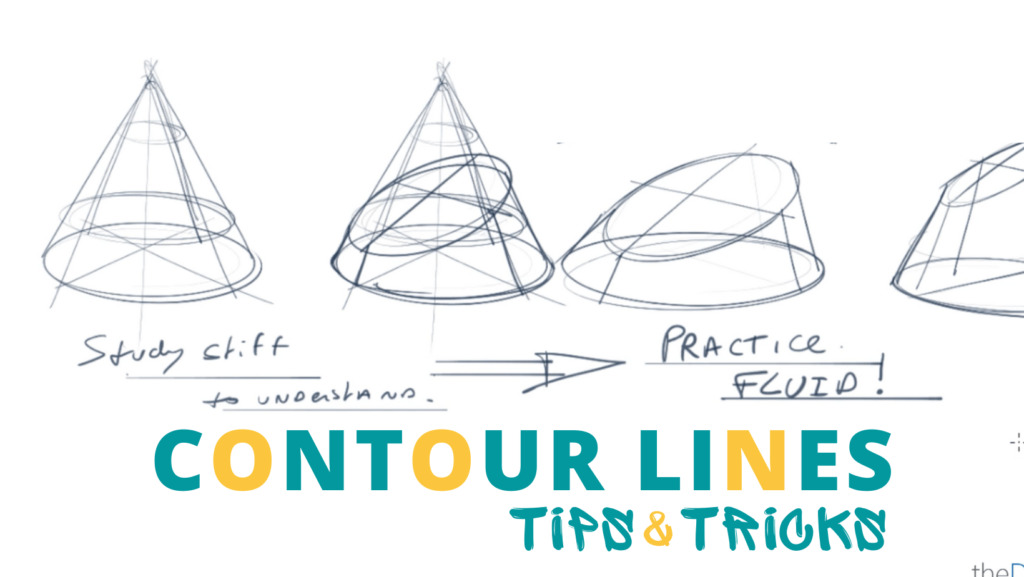
9. Contour Lines
– imaginary lines that show the volume of a 3D form.
10. Gesture drawing
- A quick, loose drawing used to capture the movement and energy of a subject.
11. Proportion
- The relationship between the size and placement of different elements in a drawing.
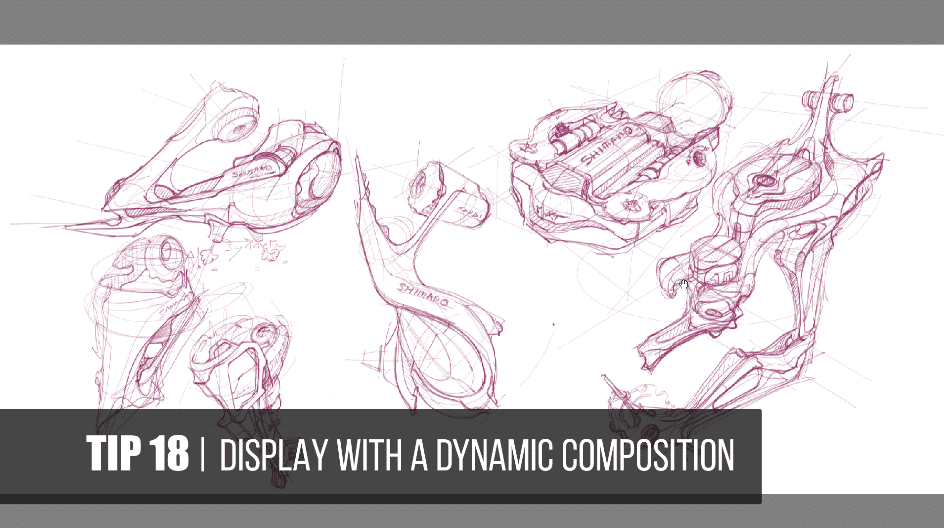
12. Composition
- The arrangement of elements in a drawing to create a pleasing and balanced image.
13. Balance
– the distribution of visual weight in a drawing to create a sense of stability.
14. Contrast
– the use of opposing values, colors, or textures to create visual interest and emphasis.
15. Texture
– the surface quality of a material or object, often represented in a drawing through the use of shading and hatching.
16. Form
– the three-dimensional shape of an object, often represented in a drawing through the use of contour lines and/or shading in perspective.
17. Scale
– the size of an object in relation to other objects or the environment in which it is placed.
18. Foreshortening
– a technique used in perspective drawing to create the illusion of an object receding into the distance.
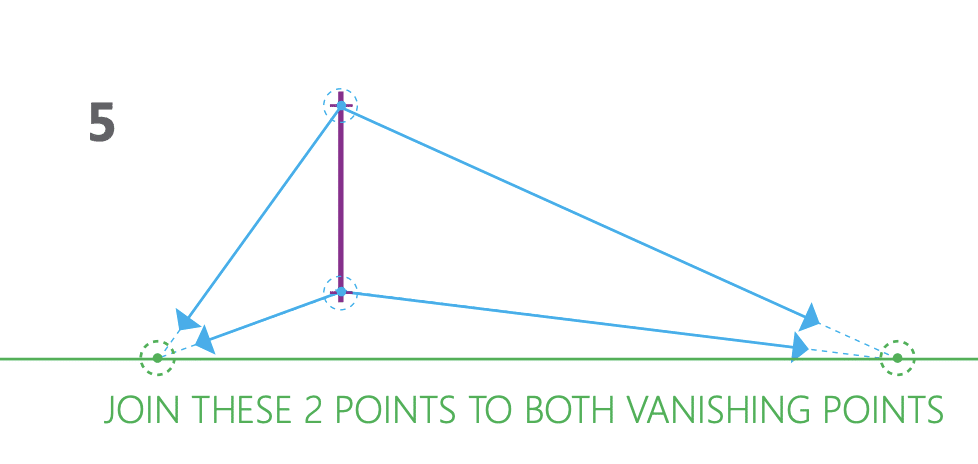
19. Vanishing point
– a point on the horizon line where parallel lines appear to converge in a perspective drawing.
20. Horizon line
– a horizontal line that represents the viewer’s eye level in a perspective drawing.
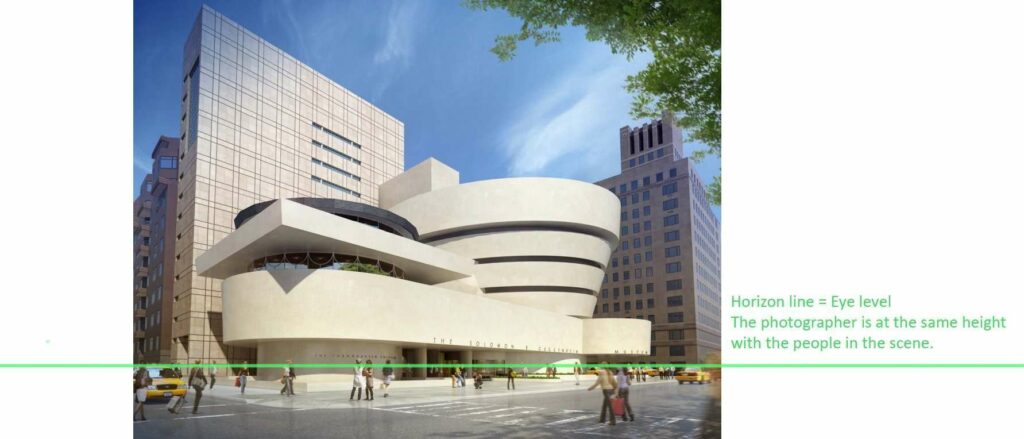

21. Eye level
– the height at which the viewer’s eyes are located in a perspective drawing.
22. One-point perspective
– a type of perspective drawing in which all parallel lines appear to converge at a single vanishing point.
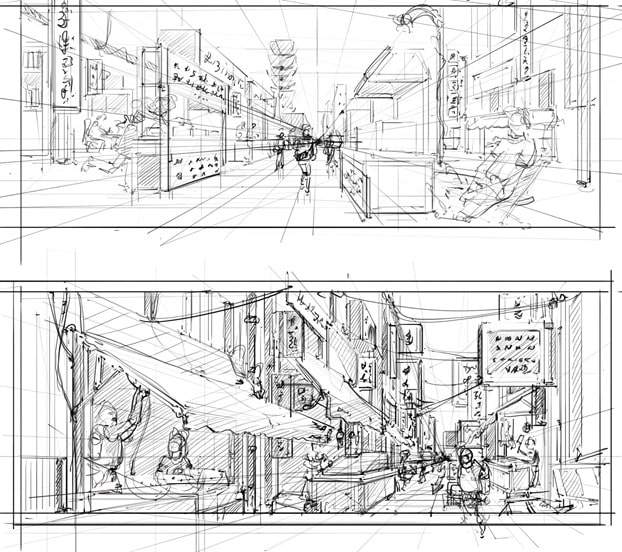
23. Two-point perspective
– a type of perspective drawing in which parallel lines appear to converge at two different vanishing points.
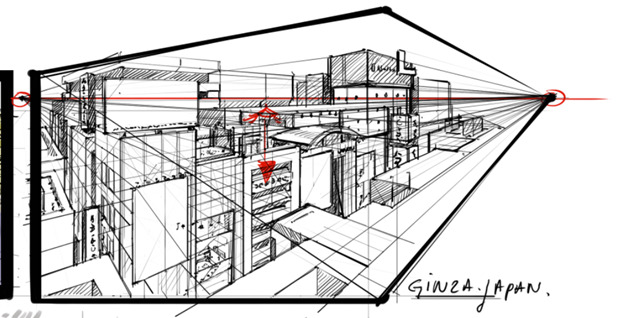
24. Three-point perspective
– a type of perspective drawing in which parallel lines appear to converge at three different vanishing points.
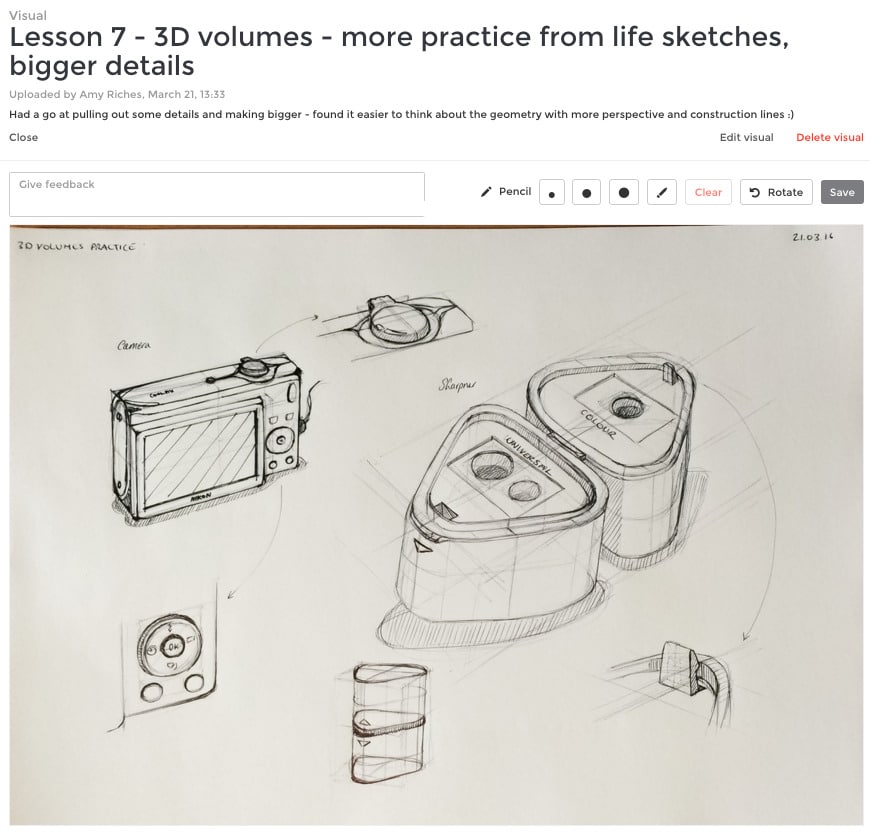
25. Isometric drawing
– a type of drawing in which all three dimensions of an object are shown in a single view.
26. Exploded view
– a drawing that shows the individual components of an object separated from each other to illustrate how they fit together.
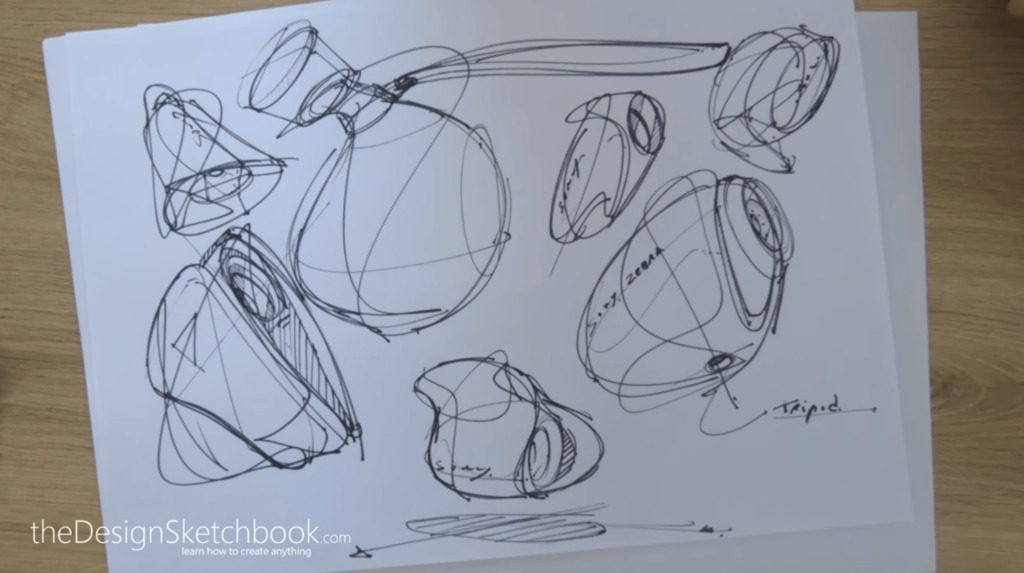
27. Design sketch
– a drawing used to explore and develop ideas for a product or object.
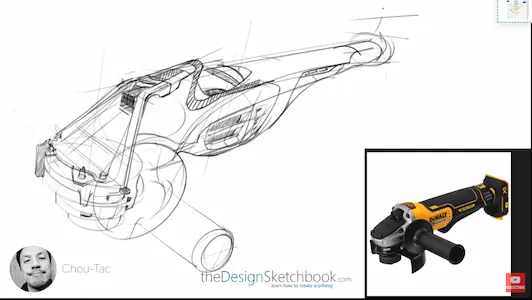
28. Concept sketch
– a drawing used to communicate a design concept or idea.
29. Rendering
– a highly detailed drawing used to show the final appearance of a product or object.
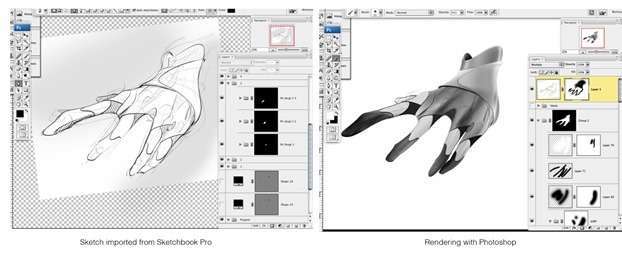
30. Marker rendering
– a technique of rendering using alcohol-based markers to create smooth, even tones and gradients.
31. Digital sketching
– the use of digital tools such as a tablet and stylus to create sketches and drawings.

32. Sketchbook
– a book used for sketching and drawing.
33. Tracing
– the process of copying a drawing by placing a sheet of paper over the original and tracing the lines.
34. Lightbox
– a device used for tracing or transferring drawings by illuminating the original through a translucent surface.
35. Perspective grid
– a grid used to help create accurate perspective drawings.
36. Reference photo
– a photograph used as a reference for a drawing or sketch.
37. Thumbnail sheet
– a sheet of paper with multiple small thumbnail sketches used to explore and develop ideas.
38. Quick sketch
– a fast, loose drawing used to capture the essence of a subject.
39. Detail drawing
– a drawing that focuses on the specific details and features of an object.
40. Marker sketch
– a quick sketch done with markers to capture the essence of a subject.
41. Sketch model
– a physical model used to explore and develop design ideas.
42. Design iteration
– the process of refining and improving a design through multiple iterations.
43. Mockup
– a physical prototype used to test and refine a design.
44. User testing
– the process of testing a product or design with users to identify and address issues.
45. Rapid prototyping
– the use of 3D printing or other rapid manufacturing techniques to quickly create physical prototypes.
46. CAD
– computer-aided design, the use of software to create and manipulate digital models of objects and products.
47. Wireframe –
a simplified 3D model used to show the basic structure and layout of an object or product.
48. Sketching tablet
– a digital tablet used for sketching and drawing.
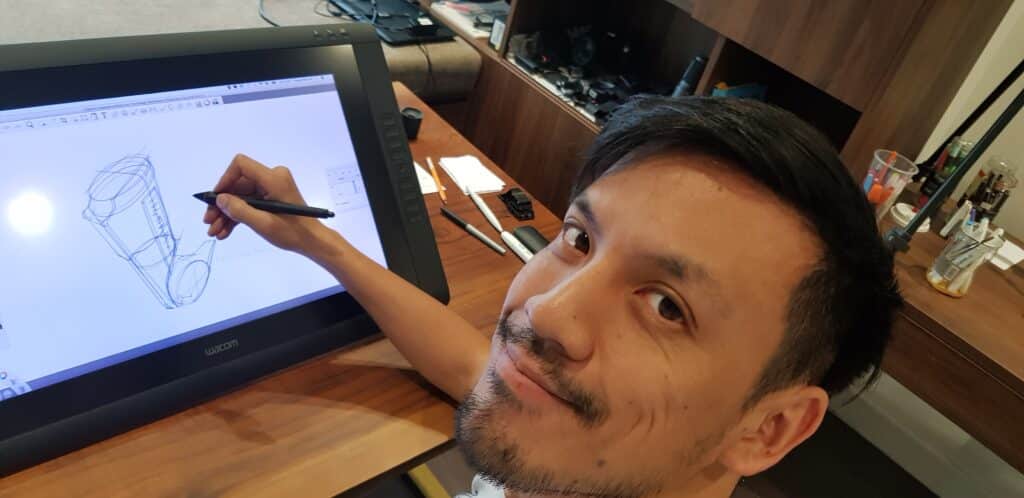

49. Digital pen
– a stylus used for drawing and sketching on a digital tablet.
50. Digital eraser
– a tool used to erase digital marks and lines.
51. Digital brush
– a tool used to create digital brushstrokes and textures.
52. Digital paint
– a tool used to apply digital paint and color to a drawing or sketch.
53. Layer
– a digital tool used to separate and organize different elements of a drawing or sketch.
54. Mask
– a digital tool used to hide or reveal specific parts of a drawing or sketch.
55. Gradient
– a digital tool used to create smooth transitions between colors or values.
56. Clipping mask
– a digital tool used to mask a layer to a specific shape or area.
57. Vector
– a digital format used to create scalable, resolution-independent graphics.

58. Bitmap
– a digital format used to create images made up of pixels.
59. DPI
– dots per inch, a measure of the resolution of a digital image or print.
60. Resolution
– the number of pixels or dots per inch in a digital image or print.
61. Color space
– a system used to define and organize colors, such as RGB or CMYK.
62. Hue
– the specific color of an object or element.
63. Saturation
– the intensity or purity of a color.
64. Value
– the lightness or darkness of a color.
65. Tint
– a color mixed with white to create a lighter shade.
66. Shade
– a color mixed with black to create a darker shade.
67. Analogous colors
– colors that are adjacent to each other on the color wheel.
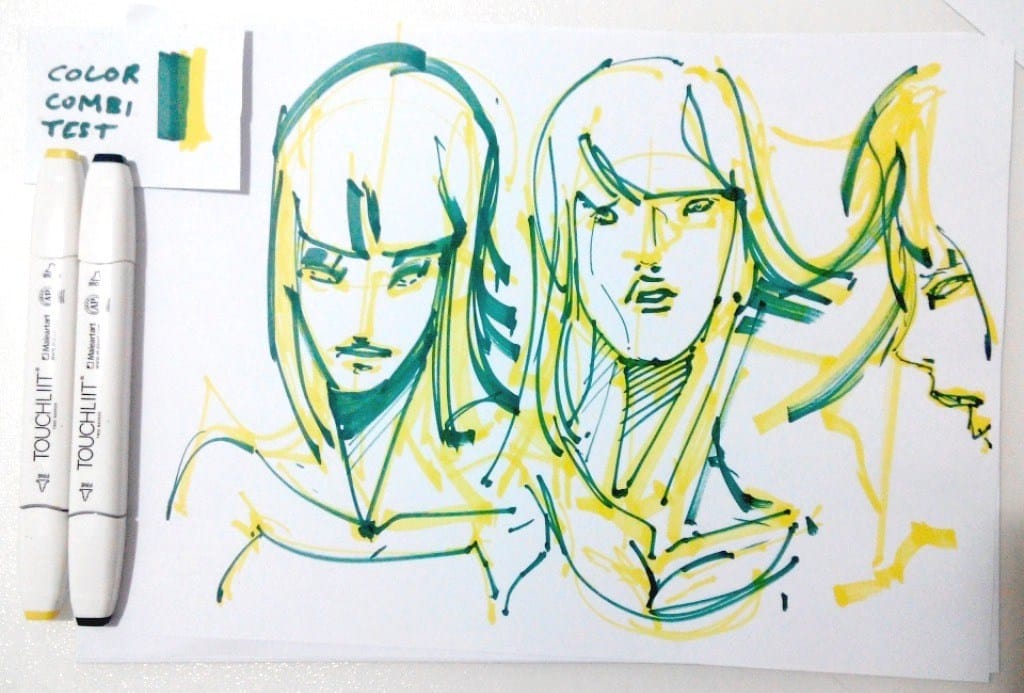

68. Complementary colors
– colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel.
69. Warm colors
– colors that are associated with warmth and energy, such as red, orange, and yellow.
70. Cool colors
– colors that are associated with coolness and calmness, such as blue, green, and purple.
71. Monochromatic
– a color scheme based on variations of a single color.
72. Triadic
– a color scheme based on three colors equidistant from each other on the color wheel.
73. Tetradic
– a color scheme based on four colors arranged into two complementary pairs.
74. Split-complementary
– a color scheme based on a base color and two colors adjacent to its complement.
75. Analogous-complementary
– a color scheme based on three analogous colors and their complement.
76. Color harmony
– the use of color schemes and combinations to create a pleasing and balanced image.
77. Color contrast
– the use of opposing colors or values to create visual interest and emphasis.
78. Color temperature
– the perceived warmth or coolness of a color.
79. Color psychology
– the study of how colors affect human emotions and behavior.
80. Materiality
– the physical properties and characteristics of materials used in design.
81. Texture mapping
– the process of applying a digital texture or pattern to a 3D model.
82. Material library
– a collection of digital materials and textures used in 3D modeling and rendering.
83. Reflection
– the way that light bounces off a surface and is reflected back to the viewer.
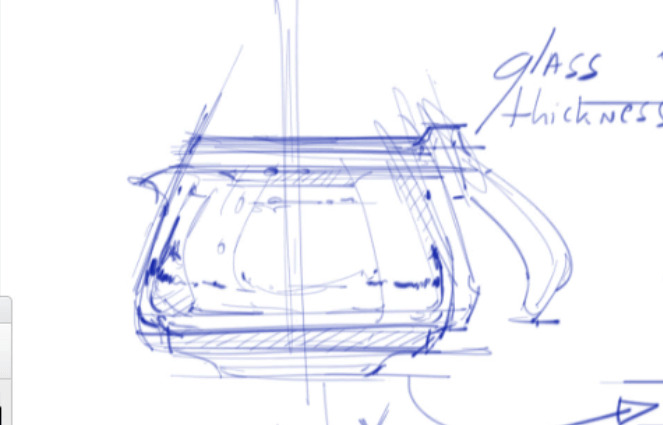
84. Refraction
– the way that light bends as it passes through a transparent or translucent material.
85. Transparency
– the degree to which an object or material allows light to pass through it.
86. Opacity
– the degree to which an object or material blocks light from passing through it.
87. Gloss
– the degree of shininess or reflectivity of a surface.
88. Matte
– the degree of dullness or lack of reflectivity of a surface.
89. Finish
– the surface treatment or coating applied to a material to alter its appearance or properties.
90. Texture mapping
– the process of applying a digital texture or pattern to a 3D model.
91. Material library
– a collection of digital materials and textures used in 3D modeling and rendering.
92. Ergonomics
– the study of how people interact with products and environments, and the design of products and environments to optimize that interaction.
93. Human factors
– the study of how people interact with products and environments, and the design of products and environments to optimize that interaction.
94. Usability
– the degree to which a product or system is easy to use and understand.
95. Urban sketching
- Urban sketching is a form of visual storytelling where an artist uses pen, pencil, or other drawing tools to depict scenes from everyday life in a city, urban environment, or sometimes even in a natural or rural environment
96. Transport design
- Transport design is the creation of innovative and problem-solving models for vehicles, such as cars, aircraft, spacecraft, or marine vessels, with an emphasis on style, comfort, branding, safety, and function.

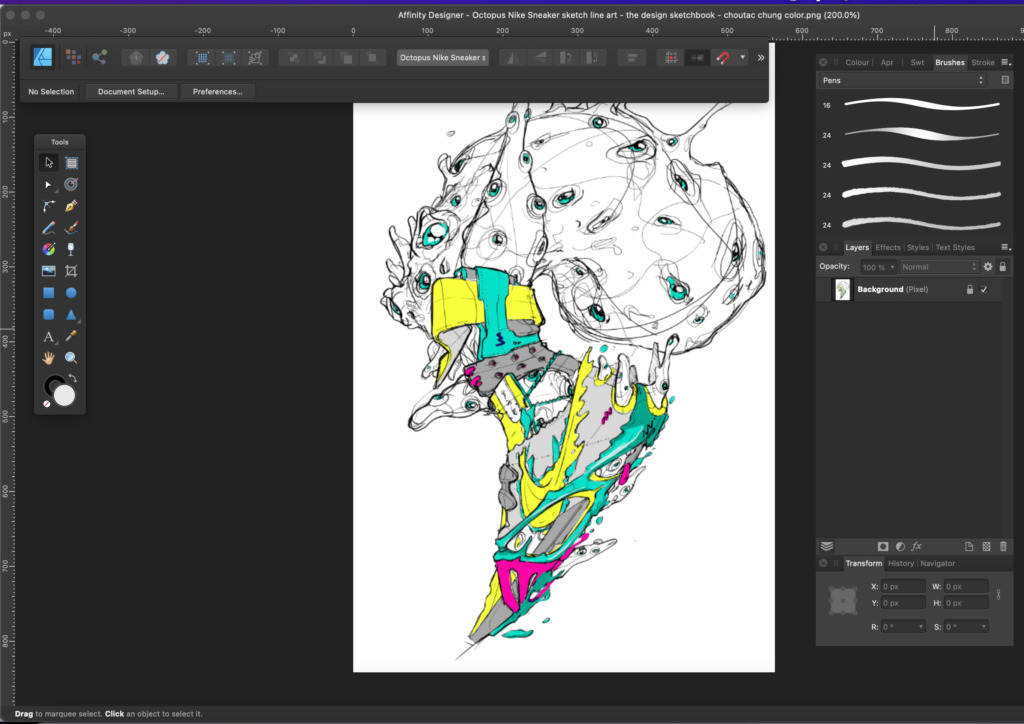
96. Sneaker design / Footwear design
- A sneaker designer is a professional who uses their advanced knowledge of materials, fashion trends, and styles to develop, create, and design sneakers for different product lines.
- They are responsible for the entire design process, from conceptualization of the original design idea to delivery of the final product.
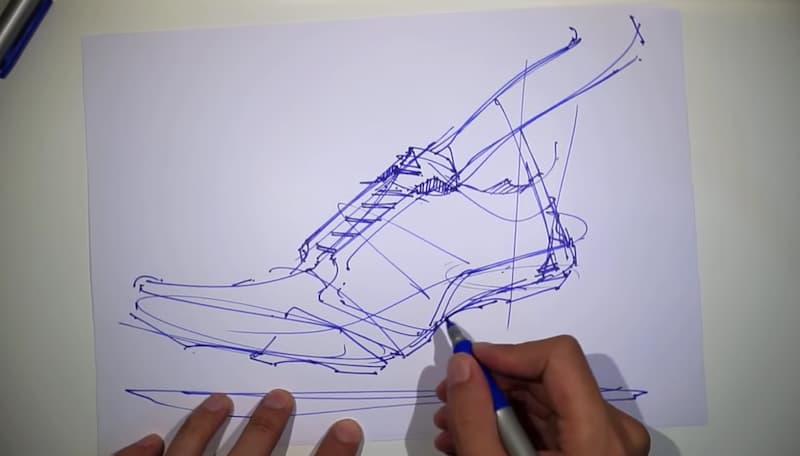
97. Fashion design
- Fashion design is the art of applying design, aesthetics, clothing construction and natural beauty to clothing and its accessories.
- It is influenced by culture and different trends, and has varied over time and place

98. Product design / Industrial design
- Product design is the process of creating, iterating, and refining products that solve users’ problems or address specific needs in a given market.
- It involves understanding the end-user customer, their habits, behaviors, frustrations, needs, and wants.
- Product designers use empathy and knowledge of their prospective customers to solve real problems for real people.
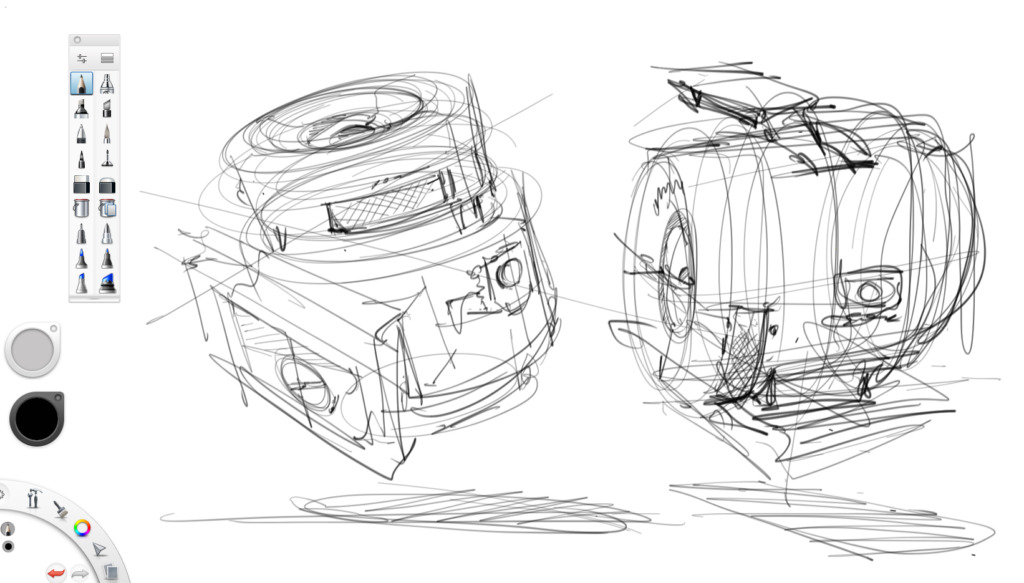
99. Concept art
- Concept art is a form of visual art used to convey an idea for use in films, video games, animation, comic books, television shows, or other media before it is put into the final product.

100. Artbook
- An “artbook” is a book that is created as a work of art in itself, often produced in small editions, and can be about art or an artist’s book, which is a form of visual art that utilizes the form of the book.
- The books with titles starting with Art of… (Name of. the movie) compile sketches of the concept drawings and inspiration.
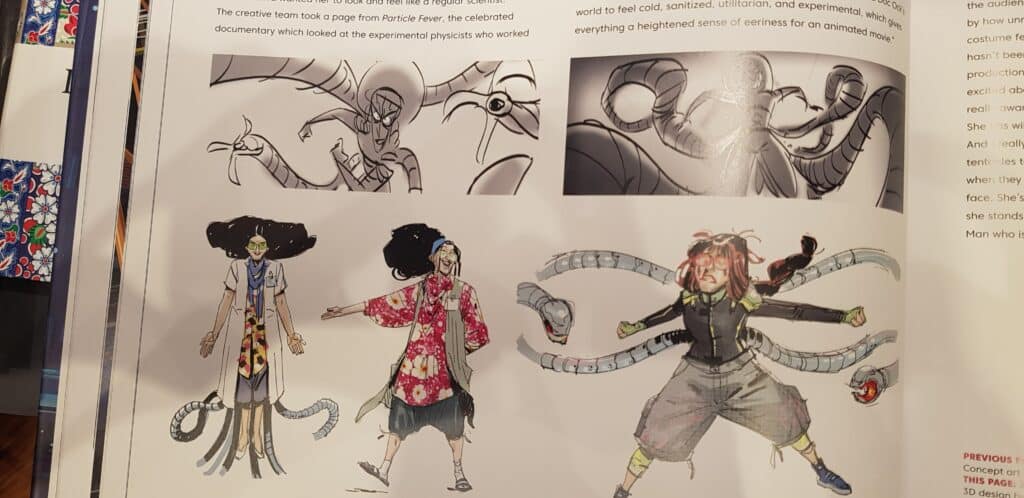

102. Toy Designer
- A toy designer is someone who creates and designs toys for children.
- They use their creativity, imagination, and knowledge of child development to make products that are fun, engaging, and safe.
- Toy designers may work independently or as part of a team at a toy company.
- Below is the artwork of Dwayne Vance, toy designer for Hot Wheels.
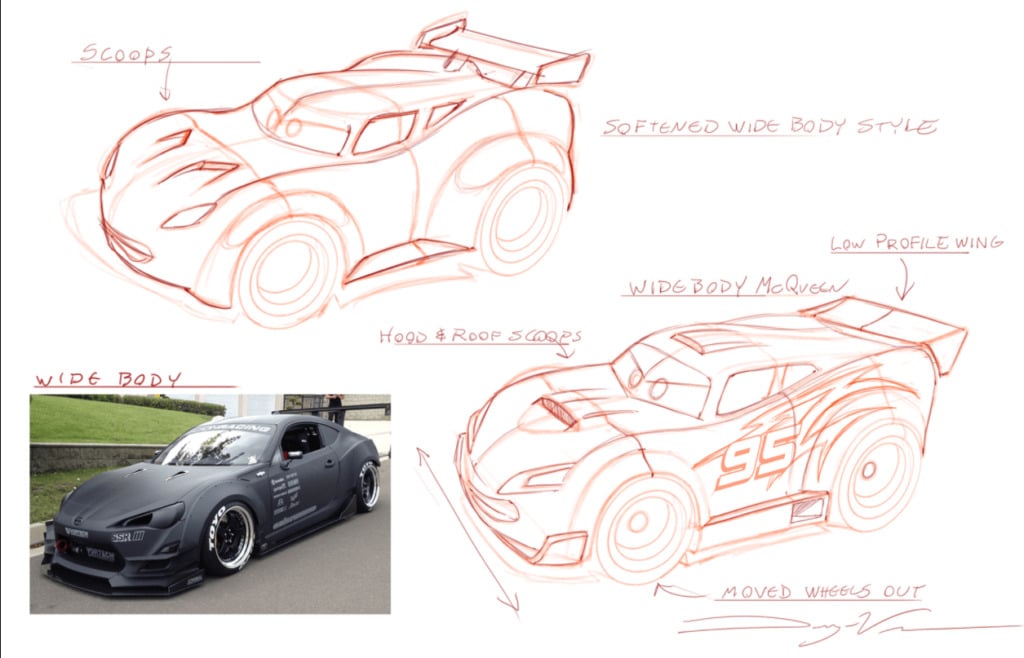
Tadaa!
This art and design terminology list is not comprehensive.
If you have any words you’d like to add, please tell me in the comments and I’ll be happy to include them!” 🎨
Cheers,
Chou-Tac






Add comment